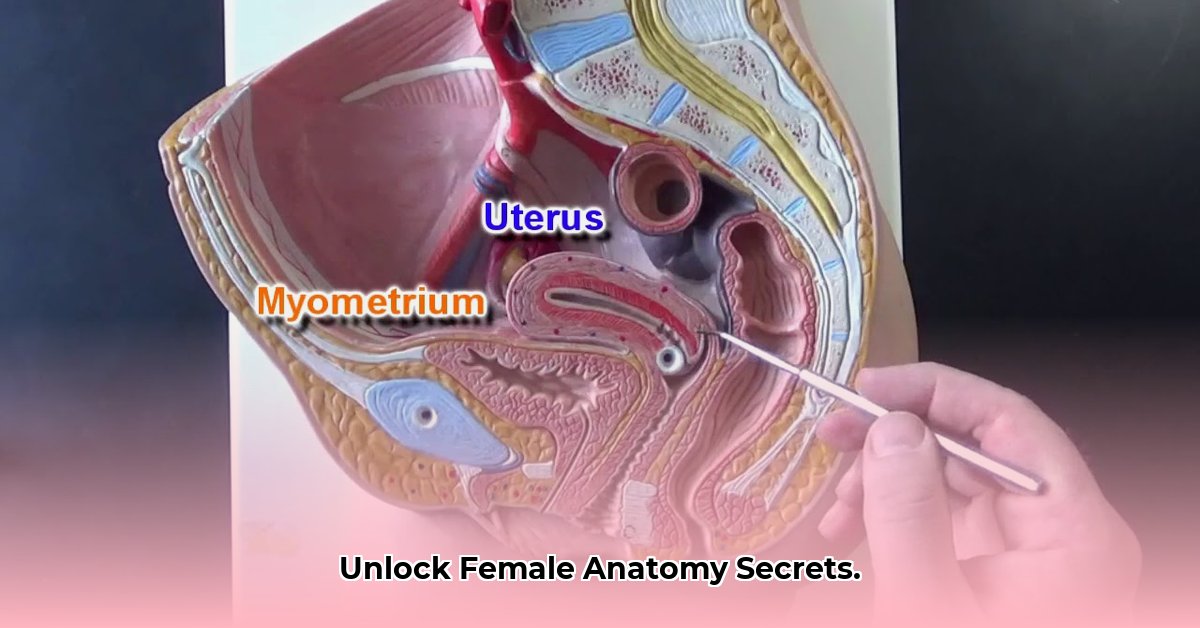
Female Reproductive System Anatomy Models: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the complexities of the female reproductive system is crucial for medical professionals, students, and even patients themselves. Traditional learning methods, while valuable, often fall short in conveying the three-dimensional relationships within this intricate system. This is where anatomical models become indispensable tools, offering a tangible and engaging way to learn and teach. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of female reproductive system anatomy models, from selecting the right model to effectively integrating it into learning and clinical practice. We'll cover different types of models, provide a step-by-step guide for selection, and offer practical tips for maximizing their educational impact. For more options, check out these female anatomy models.
Why Use Anatomical Models? The Power of Hands-On Learning
Wouldn't it be easier to understand a car engine by looking at a diagram, or by actually taking one apart and seeing how the components interact? Similarly, anatomical models offer a powerful way to grasp the complexities of the female reproductive system. Hands-on learning with these models significantly improves understanding and retention compared to solely relying on textbooks or digital resources.
Dr. Evelyn Reed, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Stanford University, states, "Studies consistently show that incorporating three-dimensional anatomical models into medical education significantly improves student performance on examinations and enhances long-term retention of anatomical knowledge." This tactile learning approach allows for a deeper understanding of spatial relationships between organs, improving clinical reasoning and patient communication.
Beyond medical education, these models are invaluable tools for patient education. A doctor's explanation is often enhanced by the ability to point to specific anatomical structures on a model, improving comprehension and building trust and confidence in their treatment.
Types of Female Reproductive System Models: A Detailed Overview
The market offers a diverse range of models, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right one depends on your specific needs and budget. Here's a breakdown of common types:
Basic Models: These models typically depict the major organs in simplified form, providing a general overview. They are ideal for introductory courses or patient education, offering affordability and ease of understanding. However, they might lack the intricate detail needed for advanced study.
Advanced Models: These high-fidelity models boast exceptional detail, often including smaller structures, ligaments, and blood vessels. While more expensive, they are perfect for in-depth study by medical professionals and advanced students.
Virtual Models: Interactive 3D software, like Visible Body, provides high-resolution renderings allowing for virtual dissection, rotation, and exploration from any angle. These digital models offer convenience and accessibility but may lack the hands-on experience of physical models.
Dissectible Models: These models allow for the removal and examination of individual organs, facilitating a deep understanding of anatomical relationships. However, they are often more fragile and require careful handling.
Selecting the Right Model: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the ideal model requires careful consideration of several factors. Follow these steps to make an informed decision:
Define Your Needs: What level of detail is necessary? Is it for introductory learning, advanced study, or patient education?
Establish Your Budget: Prices vary significantly across models, so establishing a budget early in the process is essential.
Consider the Material: Durable and easy-to-clean materials, such as PVC, are highly desirable for longevity and hygiene.
Assess Accuracy: Verify the model's accuracy against reputable anatomical references. Inaccurate models can hinder, not help, learning.
Evaluate Additional Features: Does the model allow for component removal? Are there any interactive elements? Does the size and weight suit your teaching/clinical environment?
Read Reviews: Consult reviews from educators and medical professionals before making a purchase. Their experiences can be invaluable.
| Model Type | Cost | Detail Level | Interactivity | Durability | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | Low | Low | None | High | Introductory learning, patient education |
| Advanced | Medium-High | High | Limited | High | Advanced study, medical professionals |
| Digital (e.g., Visible Body) | Subscription | Very High | High | N/A | Self-guided learning, supplement to physical models |
| Dissectible | High | High | Limited | Moderate | In-depth anatomical understanding |
Integrating Models into Curriculum and Clinical Practice
Effective integration of anatomical models requires strategic planning. Don't just display the model; use it to facilitate active learning.
Guided Discussions: Use the model as a focal point for discussions about anatomical relationships and physiological processes.
Hands-on Activities: Incorporate small-group activities that engage students in exploring the model's features.
Visual Aids: Utilize the model during lectures to enhance visual learning and reinforce key concepts.
Patient Communication: Employ the model to visually explain complex anatomical concepts to patients, bolstering understanding and fostering trust.
Effective Model Usage: Tips and Strategies
Remember, a model is a tool, not a replacement for other learning strategies. Here are some practical tips for effective use:
Active Engagement: Guide students/patients through the model's features, and encourage hands-on exploration.
Clarifying Misconceptions: Address any inaccuracies or misconceptions that may arise during the learning process.
Interactive Learning: Use the model to answer questions, stimulate discussion, and facilitate deeper understanding.
Responsible Handling: Emphasize the importance of careful handling to ensure the model's longevity.
Conclusion: Enhancing Understanding Through Tangible Learning
Anatomical models provide a powerful means of enhancing understanding of the female reproductive system. By carefully selecting and strategically integrating these models into educational and clinical settings, we can significantly improve learning, improve patient communication, and build a stronger foundation of anatomical knowledge. The benefits of hands-on learning are clear – a model is more than just a visual aid; it's a key to unlocking a deeper and more lasting understanding of this complex system.